When Vladimir Putin made a four-day journey to go to Xi Jinping in September, he addressed his Chinese language counterpart as a “expensive good friend”.
Talking to Xi throughout an enormous show of orchids in Beijing’s Nice Corridor of the Individuals, the Russian president claimed their ties had been “at an unprecedentedly excessive degree”.
Actually on the floor it seems China’s alliance with Russia has solely grown stronger since Putin’s invasion of Ukraine in 2022.
Nowhere has this been extra evident than when taking a look at commerce between the 2 international locations, which has boomed ever because the West slapped Putin with large sanctions.
Final 12 months, the worth of commerce between Russia and China hit a report $245bn (£182bn), fuelled by Xi turning into the world’s largest purchaser of Putin’s oil and gasoline. General, China additionally grew to become Russia’s largest provider of products.
Nonetheless, nearer ties with China have come at a price.
Specifically, Russian companies have grown more and more pissed off at a flood of low cost Chinese language items.
Vladimir Milov, who labored within the Russian authorities from 1997 to 2002 earlier than turning into a vocal Putin critic, says the financial alliance is backfiring badly for Russia.
“It’s deeply disadvantageous,” he says. “China is taking benefit as a result of it is aware of that Russia has nowhere to go.”
Such warnings may sign that the financial ties between the 2 international locations are starting to fray.
Whereas mutual commerce hit a report excessive in 2024, it has fallen by almost a tenth to this point this 12 months.
Lada gross sales plunge
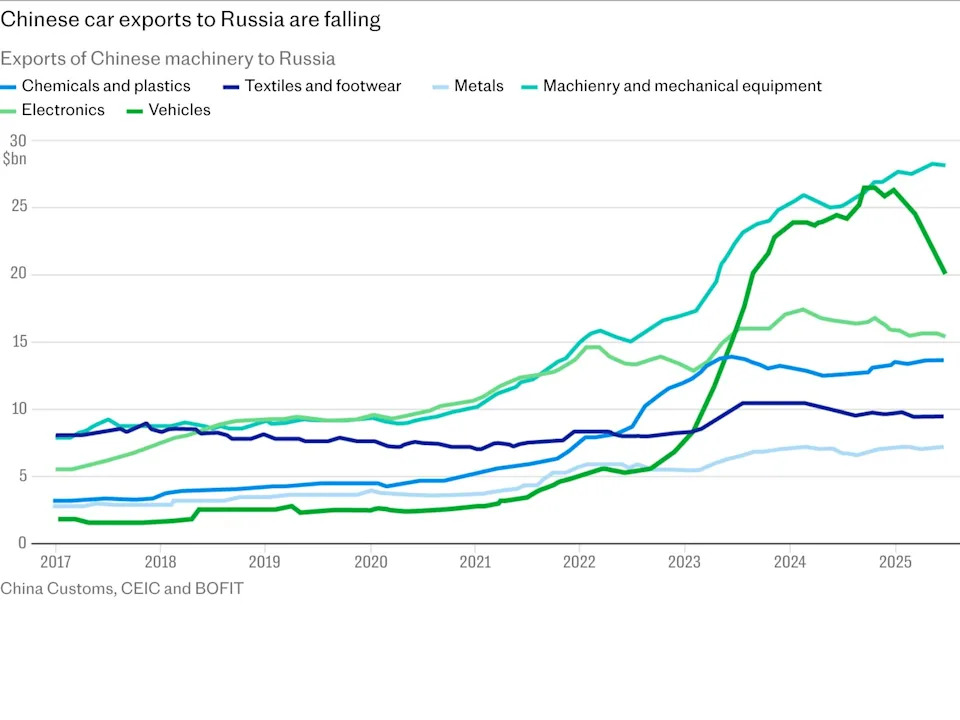
One key space of stress is vehicles.
After Western producers minimize ties with Russia in 2022, Chinese language rivals duly stepped in.
Within the two years to 2024, Chinese language automobile exports to Russia have elevated sevenfold, prompting a rising variety of complaints from home producers.
Maxim Sokolov, the chief government of Russian carmaker AvtoVAZ, has accused the Chinese language of “unprecedented dumping”, which he stated in December has crossed “all possible boundaries”.
Gross sales of his firm’s signature Lada automobile have plunged, pushing the corporate to slash manufacturing by almost half and transfer to a four-day work week on the finish of September.
Gross sales of AvtoVAZ’s signature Lada vehicles have plunged, prompting it to halve manufacturing – Andrei Bok/SOPA Photographs/LightRocket through Getty Photographs
Russia’s largest truck producer, Kamaz, additionally trimmed its working week in August after demand for its autos plunged by 60pc. On the time it blamed “extreme” imports.
To alleviate a few of the criticism, the Kremlin has responded by considerably elevating import charges on autos.
Since October 2024, Russia has greater than doubled the “recycling payment” that it costs on imported vehicles.
This cost, which is supposedly to cowl the longer term disposal of the automobile however features largely as a tariff, was 667,000 roubles (£6,275) per automobile as of January this 12 months.
This led to Chinese language automobile exports to Russia halving within the first six months of 2025.
b’
1912 China’s automobile exports to Russia
‘
In July, Russian regulators additionally banned truck imports from a fleet of main Chinese language manufacturers – Dongfeng, Foton, FAW and Sitrak – which they branded a “direct risk” to public security.
“These trade-related tensions will begin to happen an increasing number of because the market will get saturated with Chinese language items and uncompetitive Russian industries usually are not capable of make their gross sales,” says John Kennedy, a analysis chief at Rand.
Sanctions chunk
There are indicators that Russia’s metal sector can be hurting.
Andrey Gartung, chief government of the Chelyabinsk Forging and Press Plant, warned final 12 months: “Russian enterprises competing with Chinese language ones are holding on by the pores and skin of their enamel.”
Not one to shrink back, China has hit again with commerce restrictions of its personal.
Most notably, Xi reintroduced tariffs on Russian coal in January 2024, two years after the restrictions had been first lifted.
This has already hit exports to China, with Milov claiming that the levies are including to what’s the worst disaster for Russia’s coal trade because the collapse of the Soviet Union.
The sector’s revenues are anticipated to plummet by 12pc this 12 months alone.
Elsewhere, China has to this point refused to carry a longstanding ban on imports of Russia’s largest agricultural exports – winter wheat and barley. As an alternative, it buys from Ukraine and Kazakhstan.
What China does import from Russia, it will get extremely cheaply as a result of it has a monopoly as one in all Russia’s solely patrons, says Milov.
Russia’s largest exports to China are oil and gasoline, which mixed make up two thirds of its commerce.
Igor Sechin, Rosneft’s chief government, stated that between January 2022 and June 2024, China’s financial savings from buying Russian oil in comparison with Center Japanese exports amounted to as a lot as $18bn.
“Taking the sanctions away, Russia is what Beijing would need each buying and selling associate to seem like,” says Gregor Sebastian, of Rhodium’s China Company Advisory workforce.
“China is importing uncooked supplies that it produces into manufactured items that it might probably then resell at a lot increased revenue margins again to Russia. That’s the major bulk of the connection.”
Nonetheless, greater than something, Russia desires new expertise and funding from China. And it’s not getting it.
Joint initiatives stall
The typical annual stream of Chinese language funding into Russia has plummeted from a median of $1.2bn from 2011 to $400m, says Milov.
In 2022, China dropped Russia from its Belt and Highway financing programme, whereas in July, China’s commerce ministry “strongly suggested” carmakers towards investing in Russia.
Many main initiatives that had been beforehand introduced with Chinese language backing have now been scrapped or are on maintain.
Russia quietly disappeared from what was speculated to be a joint growth of a long-haul plane with the Business Plane Company of China.
Work had already begun on the venture, initially known as the CR929, which stood for “China Russia”. Nonetheless, the R has now been dropped, with the plane renamed because the C929.
Plans for Chinese language CRRC Changchun Railway Automobiles to construct a high-speed rail line between Moscow and Kazan in south-west Russia have additionally been paused.
Individually, there was no progress on the event of the Tianjin oil refinery, a three way partnership between Rosneft and the Chinese language Nationwide Petroleum Company (CNPC), which was accepted in 2014.
After the assembly between Putin and Xi in September, Gazprom introduced that the 2 international locations had signed a deal to construct a “Energy of Siberia 2” gasoline pipeline to China.
However whereas this might little doubt show to be an enormous victory for Russia, China has but to verify the venture.
This can be an indication that, for all of the pomp and ceremony, the international locations’ authoritarian alliance could also be weaker than it seems.
“Regardless of all these hugs and kisses at summits, China and Russia are very a lot far aside,” says Milov.
Strive full entry to The Telegraph free right this moment. Unlock their award-winning web site and important information app, plus helpful instruments and professional guides in your cash, well being and holidays.